Seawater desalination is an important issue to address freshwater scarcity and meet arid areas’ water supply needs. With the increasing demand for domestic water, finding an effective way to supply clean water from seawater becomes urgent. Refer to the information in the following article from ATS Water Technology to gain a deeper understanding of the process of desalinating seawater!
1. What is seawater desalination?
Seawater desalination is a technological process that transforms seawater into low salinity water (desalination), suitable for various purposes. The seawater treatment technology process includes steps such as debris filtration, salt separation, disinfection, and pH adjustment and minerals balancing. The resulting freshwater meets quality standards and can be used for domestic purposes, agricultural irrigation, or industrial applications.

2. Seawater desalination technologies
Freshwater resources are increasingly scarce, making seawater desalination to produce fresh water becomes essential. So what is the method of filtering fresh water from seawater that we want to share with you? Please follow the content below to understand in more detail how to process seawater into fresh water.
2.1. RO membrane
Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology is a widely used water filtration process to produce fresh water from saline water, especially seawater. At the core of this process is the RO membrane system.
Made from polymer materials with molecular-selective capabilities, the RO membrane features a tiny porous structure that selectively allows water molecules to pass through while blocking salt ions, larger molecules, and more. Typically, the pore size of an RO membrane is about 0.0001 μm.
During the filtration process, saline water, like seawater, is pushed through the RO membrane under high pressure. This pressure enables water molecules to permeate the RO membrane, resulting in obtaining nearly salt-free and impurity-free pure water.
RO membrane technology is capable of eliminating 99.89% of salts, heavy metal ions, large organic molecules, and most disease-causing microorganisms in water. The output is high-quality fresh water suitable for both domestic and industrial applications.

2.2. Seawater distillation
Distillation is one of the effective methods of turning seawater into fresh water. It relies on using high temperatures to evaporate water from seawater, then cooling the vapor to separate the fresh water.
The process begins when seawater is fed into a specialized distillation apparatus. Within this system, the temperature is raised to boil the seawater. As the water boils, water vapor is created and separated from other substances in the seawater like salts and other dissolved substances. The water vapor then passes through a cooling system, where it is chilled by cold water or air, resulting in pure water.
The distillation process not only removes salt and impurities from seawater but also results in purified water. It effectively eliminates dust particles, bacteria, and other dissolved contaminants during the process.
However, this process requires a significant amount of thermal energy to reach the necessary temperatures for boiling seawater and evaporating the water. As a result, distillation is typically used in industrial applications where a reliable thermal energy source is available.
3. Seawater treatment technology process
RO membrane systems are the most commonly used for seawater treatment due to their high salt rejection rate up to 99.89% and lower energy consumption compared to other methods. They also offer high capacity, flexible design, and minimal environmental impact. The process of converting seawater into domestic water or fresh water using RO seawater filtration system involves the following stages:

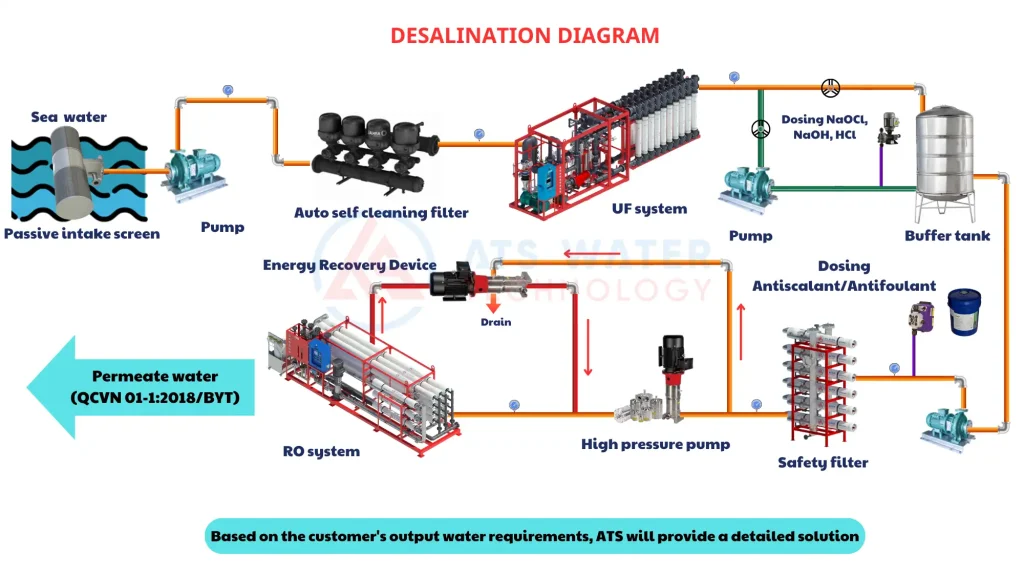
3.1. Seawater intake stage
The seawater intake stage is crucial as it determines the quality of the water entering the entire subsequent treatment process. To ensure a stable quality of seawater, facilities utilize advanced automated intake systems like Johnson Screens Passive Intake.
This system features protective filter screens that remove large impurities such as debris and algae from the seawater right from the start. The advantage of this equipment is its self-cleaning technology, making it ideal for operation in hard-to-reach areas with high levels of debris, trash, and sediment in the water environment.
Thanks to this efficient intake system, the original seawater is pre-treated to ensure stable quality before proceeding to the subsequent technical treatment stages.
3.2. Seawater treatment stage
Explore the intricate process of this phase, from removing salt and impurities to producing fresh, safe water for use, in the following content:
3.2.1. Preprocessing stage
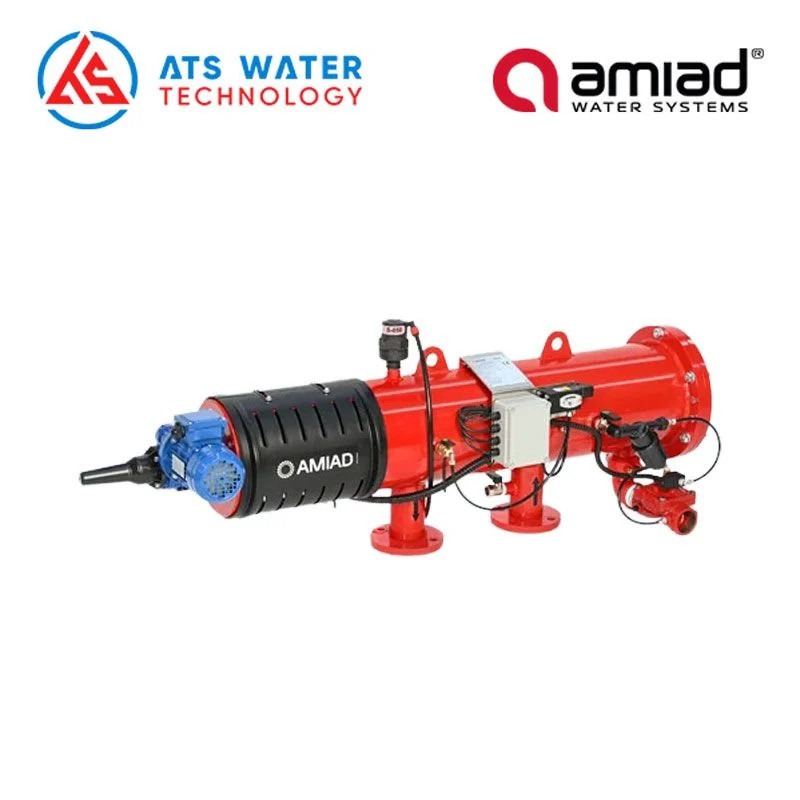
- Amiad Auto Self-Cleaning Filter: Seawater from the storage tank is pumped through the Amiad self-cleaning filter with a filtration size of 100 μm. This device plays a crucial role in removing large suspended solids from water, protecting the ultrafiltration (UF) system in the next stage from clogging.
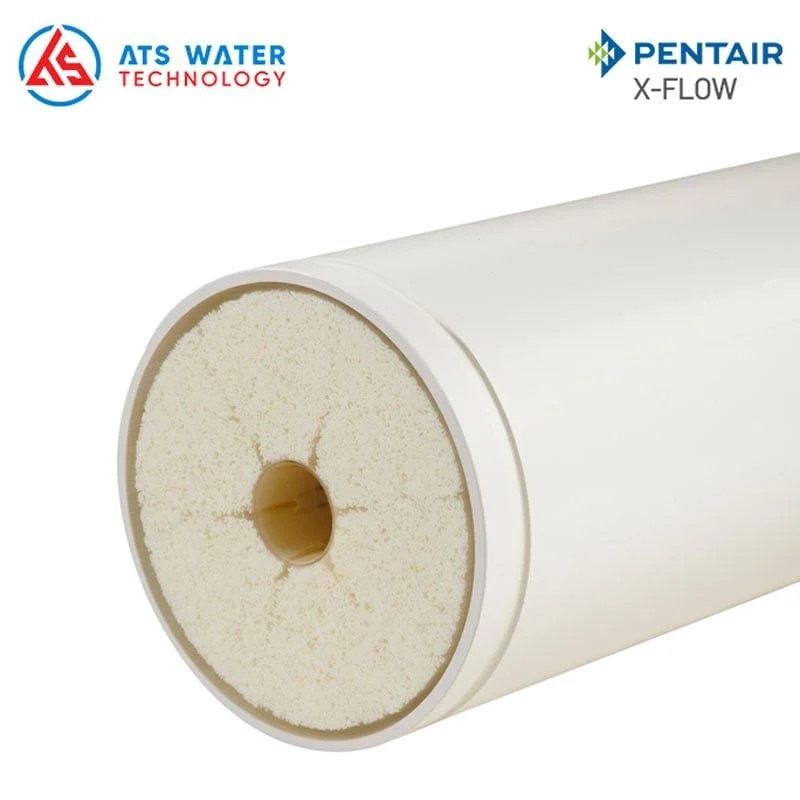
- Pentair X-Flow UF Membrane: After preliminary filtration, water is directed to the Pentair X-Flow UF system with ultra-fine filtration at 0.02 μm. Its unique inside-out filtration mechanism effectively eliminates bacteria, fine particles like colloids, emulsions, suspended solids, and other larger contaminants. The filtered water is stored in a tank, with a portion supplied to the RO system while the remainder is used for periodic backwashing of the UF membranes every 20 to 120 minutes to maintain optimal performance.
- Aqualine Fine Filter Equipment: Before reaching the RO system, water from the UF tank is pumped through a 5 μm fine filter to filter out any remaining dust and small particles, ensuring the protection of the high-pressure pump and RO membranes.
- iSave Energy Recovery Device: The iSave system recovers hydraulic energy from the RO system’s reject stream and recycles it back into the system, significantly reducing operational costs.
- PWT Antiscalant Chemicals: In seawater applications, SpectraGuard™ 360 is specifically used to manage scaling agents on RO membranes, such as carbonates, sulfates, phosphates, metal hydroxide, silica… as traditional softening and hardness removal methods are ineffective.
3.2.2. Main processing stage
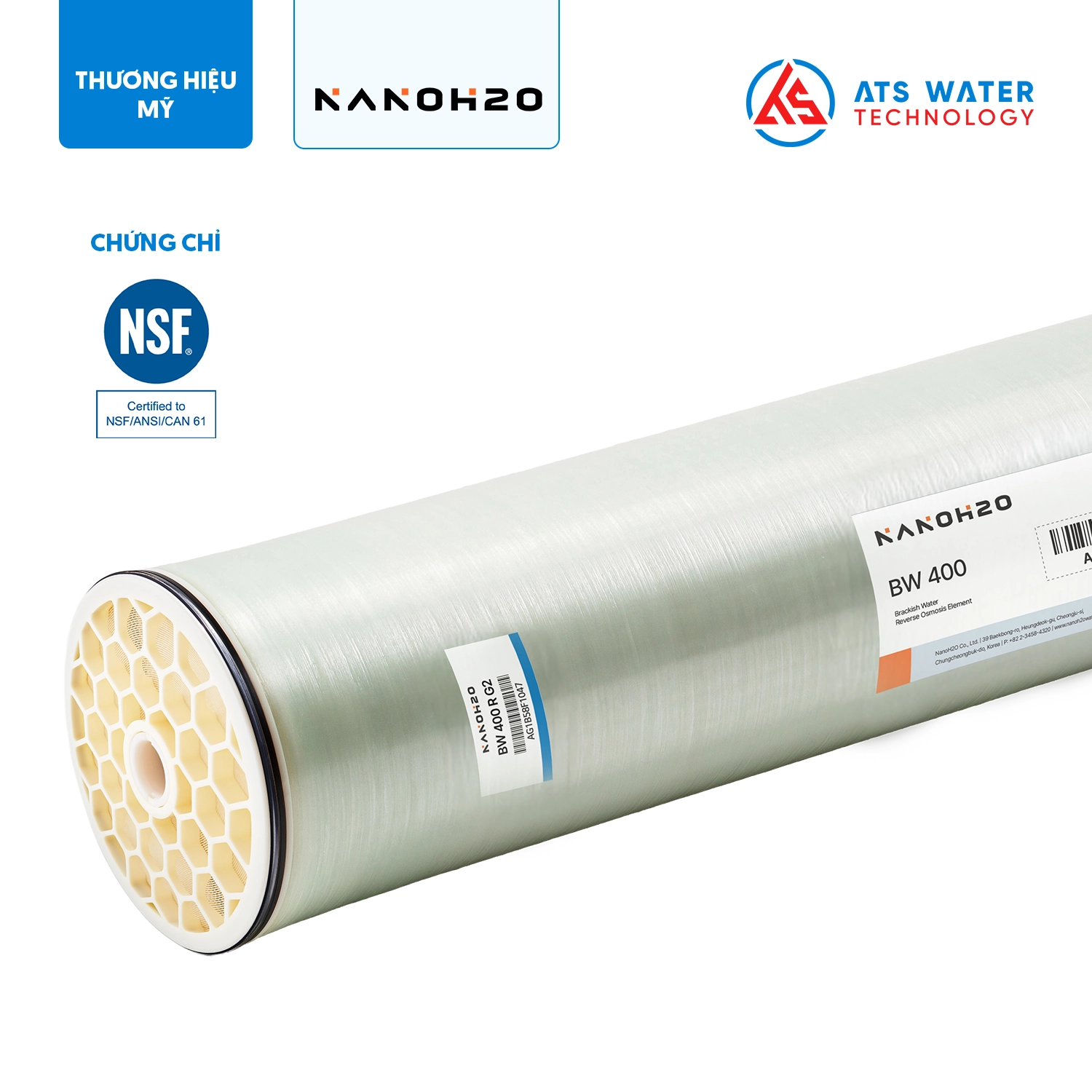
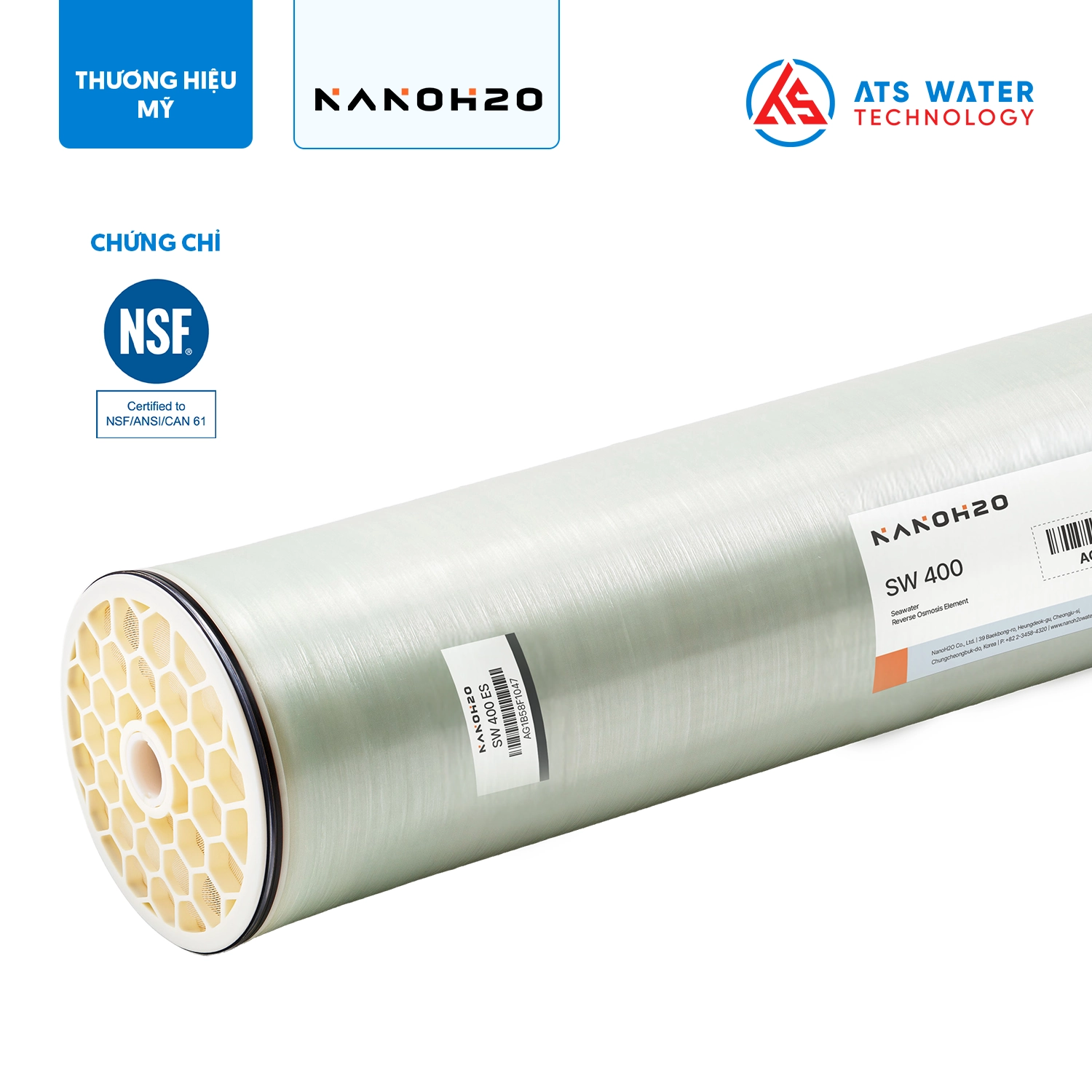
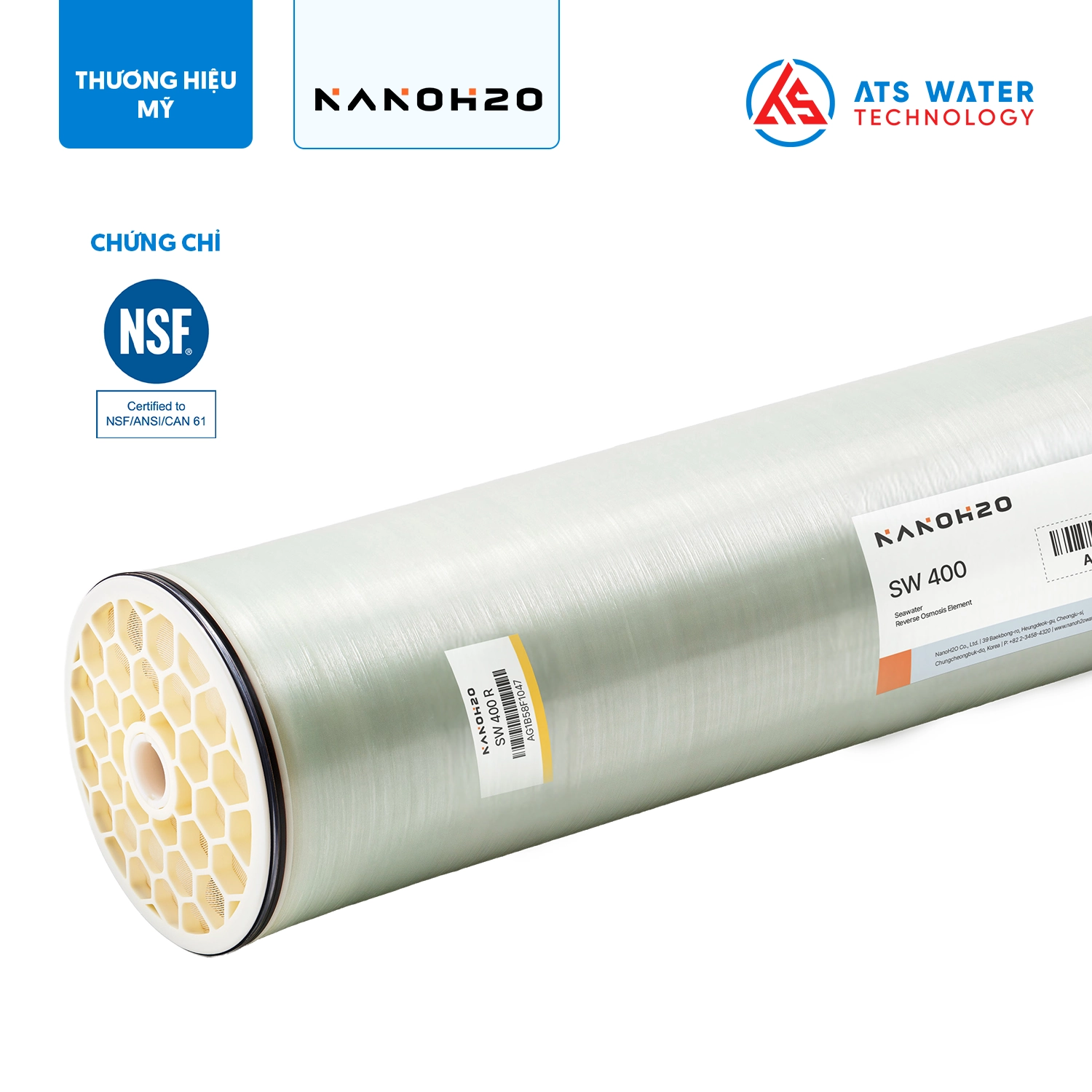
- NanoH2O RO membrane: The RO system utilizes the LG SW 400 SR membrane, which is manufactured with TFN (Thin Film Nanocomposite) technology. This membrane offers a high salt rejection rate of up to 99.89%. Seawater is pumped through the membrane under high pressure, allowing purified water to filter out through the system. The treated water complies with the quality standards for clean water as specified in QCVN 08-1:2018/BYT, making it appropriate for both domestic and industrial uses.
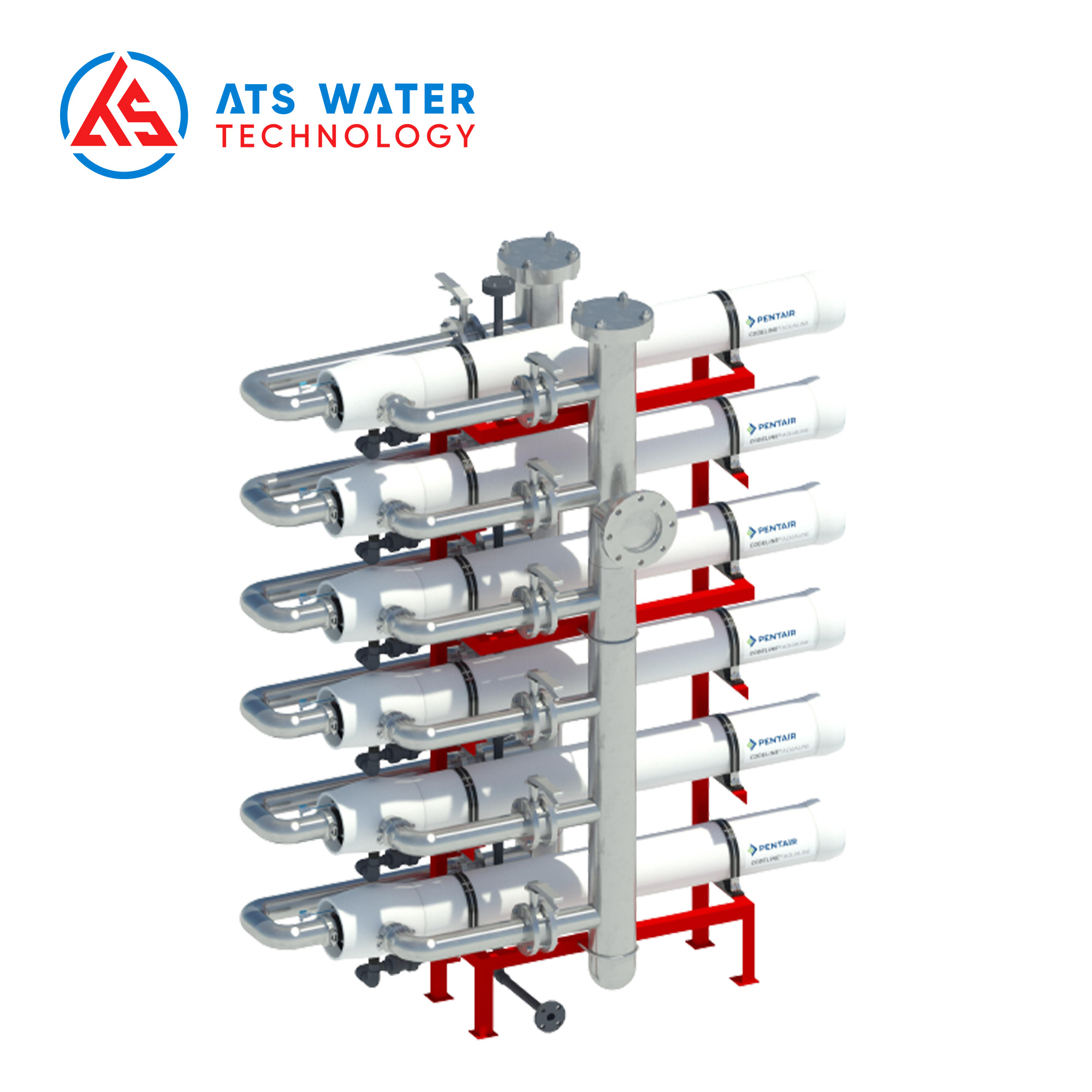
- Codeline RO membrane pressure vessel by Pentair: The Codeline RO membrane pressure vessel, manufactured by Pentair is engineered from high-grade materials to withstand high operating pressures. This housing provides robust protection for the RO membrane against external impacts and reduces the risk of water leakage during system operation.
3.3.3. System maintenance stage
- PWT membrane cleaners: Following a period of operation, the RO system requires periodic CIP (Clean In Place) to restore flow rates and treatment performance. PWT membrane cleaners are effective in removing organic fouling, biofilm, metal hydroxides (such as iron), and inorganic scale (such as CaCO3 or silica) that deposit on the RO membrane surface.
- Aqualine fine filtration equipment: During the CIP cleaning process, the Aqualine fine filtration equipment plays a crucial role in capturing and removing contaminants from the system. It prevents these particles from re-entering and affecting system performance.
4. Benefits of seawater treatment
Seawater treatment offers several significant advantages. Here are the benefits of applying this technology:
- Groundwater resource protection: Rather than overexploiting underground water sources, seawater treatment reduces stress on these valuable resources. This contributes to the conservation and sustainable management of groundwater.
- Compliance with water quality standards: Through comprehensive treatment processes, the treated seawater fully complies with the National Technical Regulations on the Domestic Water Quality (QCVN 08-1:2018/BYT), ensuring safety for public health during consumption.
- Easy operation: With a modern, user-friendly design, the latest seawater treatment systems allow for easier and more flexible operation than before. Control and monitoring procedures have been greatly streamlined.
5. Application of RO systems in seawater treatment
The application of RO systems to seawater treatment has many important uses in the following areas:
5.1. Domestic water supply station
Projects to establish domestic water supply stations using reverse osmosis (RO) membrane technology are commonly implemented in coastal regions or areas with limited access to freshwater sources.
RO technology effectively removes impurities, microorganisms, and salt from seawater, transforming it into a safe and pure water source to meet the local population’s needs for cooking and personal hygiene. The seawater treatment process using RO ensures the reliable provision of high-quality fresh water for areas that lack or have limited access to surface water.
5.2. Water treatment for thermal power plants
Water is a critical input factor for the continuous operation of thermal power plants. Reverse osmosis (RO) systems are utilized to produce high-quality ultrapure water for high-pressure boilers.
The comprehensive water treatment process includes ion exchange resin to remove impurities, degassing, and anion removal to meet the stringent water supply standards for boilers ensuring the safe and efficient operation of thermal power systems.
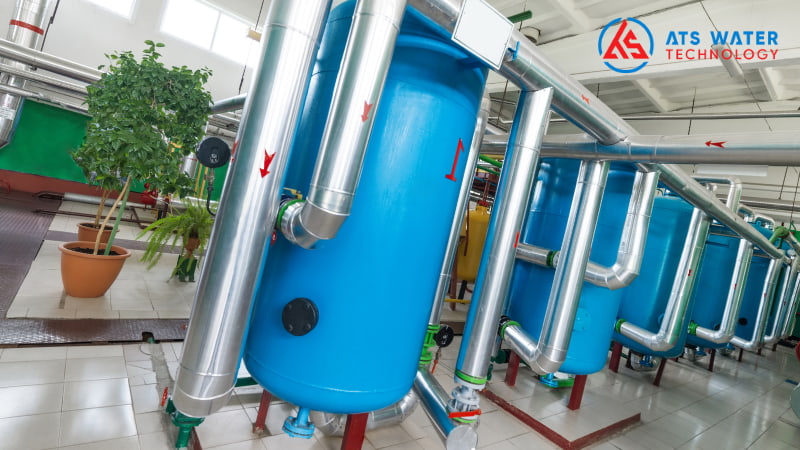

5.3. Supplying water to coastal resorts
For coastal tourism resorts, reverse osmosis (RO) technology plays a crucial role in desalinating seawater to provide clean freshwater for the needs of visitors. This process includes:
- Desalination of seawater into freshwater: Seawater is fed into the RO system, where high pressure is applied to push the water through specialized membranes. These membranes allow freshwater to pass through while retaining salts and other contaminants, producing clean freshwater for resorts.
- Freshwater supply for tourism operations: The clean water produced by the RO seawater treatment system is used to meet the daily needs of tourists staying at coastal resorts.
The application of RO technology for seawater desalination addresses the demand for freshwater in coastal resorts, while also contributing to the protection of natural freshwater resources from overexploitation.
6. Frequently asked questions
Here are some questions about seawater treatment that can be referenced:
Why is seawater treatment required before usage?
Seawater contains elevated levels of salts, so it must be treated to remove salt and impurities, ensuring safe use in human consumption and industrial application.
What is the most widely used seawater filtration technology?
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is the most popular method, using pressure to push water through the membrane that removes salt and other impurities.
What are the possible uses of treated seawater?
After treatment, seawater can be safely used for drinking, irrigation, and as cooling water for industrial systems.
Thus, seawater desalination is an important process to convert seawater into clean water suitable for various applications. For customers seeking more detailed information about these solutions, please contact us at ATS Water Technology Co. Ltd for prompt consultation via:
ATS WATER TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
- Headquarter: 54/18 Bui Quang La, Ward 12, Go Vap District, HCMC
- Branch: 77 DHT10B, Dong Hung Thuan Ward, District 12, HCMC
- Consultation and support: (028) 6258 5368 – (028) 6291 9568
- Email: info@atswatertechnology.com
- Social media: Facebook | LinkedIn | Zalo Official

































 Solution
Solution  Technology
Technology  Application
Application 




